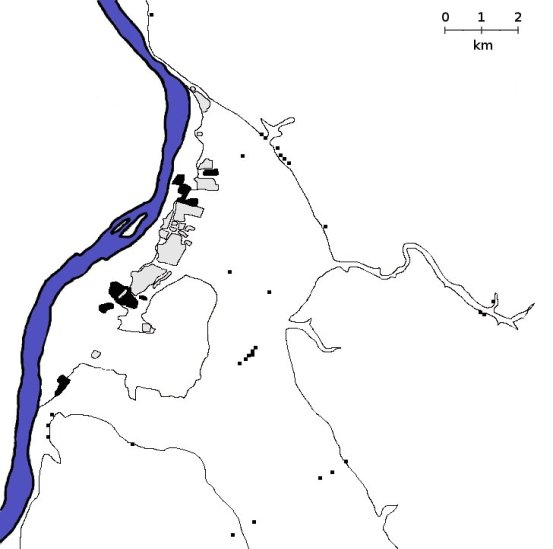
Akhenaten of the Nineteenth Dynasty built Akhetaten as the new capital city of Egypt. For the location, he chose Amarna, a fresh site on the eastern bank of the Nile, about 275 kilometers northwest of the old capital city of Thebes. After his death, the city was virtually abandoned. The degree of planning involved in the construction of Amarna involved for the most part the administrative and religious buildings of the Central City.Even the planned part of the city was somewhat hastily designed and assembled.
Most of the city was built along an eight kilometer north-south main street, referred to today as the “Royal Road,” which connected the Central City with the North City, an outlying satellite and the probable residence of the king.The king probably lived in the North Riverside Palace in the North City, a large building on the east side of the Royal Road and separate from the rest of the city, protected by a fortified wall which enclosed a complex of royal service buildings.
On the opposite side of the road from the palace lay a group of some of the largest houses in the city, probably belonging to nobles who were very close to the king. An administrative building containing an enormous warehouse formed the northern limit of the North City. At the southern end of the Royal Road lay the Central City, a group of temples, palaces, and administrative buildings forming the executive hub of the city.
The planned buildings of the Central City can be found in an inscription on one of the Amarna Boundary Stelae which marked the boundaries of the city at its founding.In it, Akhenaten describes the main buildings he will construct in his new capital:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urban_planning_in_ancient_Egypt
The use of urban planning in ancient Egypt is a matter of continuous debate. Because ancient sites usually survive only in fragments, and many ancient Egyptian ...www.theancientegyptians.com/towns.htm
Almost every aspect of the ancient Egyptians lifestyle was, in some way, affected by the River Nile. Even the planning of atown or city was done so, around the ...www.aeraweb.org/lost-city-project/walking-ancient-streets/
Neighborhoods and districts of ancient villages, towns, andcities are somewhere between town planning and self-organization. As settlements grow, there is ...- - Report images
www.touregypt.net/featurestories/cities.htm
Cities in ancient Egypt grew out of the development of agriculture and the .... made up on a grid plan and surrounded by a wall measuring some twenty feet thick.www.digitalegypt.ucl.ac.uk/house/towns.html
Nevertheless there has been an interest in town planning from the early days of ... persistent view of Ancient Egypt as a 'civilization without cities' (Wilson 1958) ...www.reshafim.org.il/ad/egypt/building/townplanning.htm
Town planning or rather the lack of it. ... Ancient Egyptian town planning: Location, city quarters, residential areas, temple districts, palaces ...[PDF]www.public.asu.edu/~mesmith9/1.../MES-07-FormMeaning.pdf
Smith / NEW APPROACH TO ANCIENT URBAN PLANNING17. Figure 9: Comparison of Semiorthogonal Urban Blocks at Amarna, Egypt (b), with a simulated. www.scribd.com/.../Ancient-Egyptian-Urban-Planning-and-Infrastructur...
Apr 23, 2011 - A Historical Lie the Stone Age > Ancient Egyptian Urban Planning and Infrastructure. Egypt's arid climate has left behind many clues to their ...harunyahya.com/en/Articles/.../ancient-egypt-a-magnificent-civilization
Jul 7, 2008 - The civilization of Ancient Egypt, which registered such great successes in medicine, especially anatomy, urban planning, architecture, fine arts ...
www.angelfire.com/ar/corei/hbe1/ancient.htm
Outline plans of Egyptian cities varied from rectangle to square (except El Amarna). Oldest settlements were oval or round: Dimensions of city plans were always ...
Our Photos of Egypt